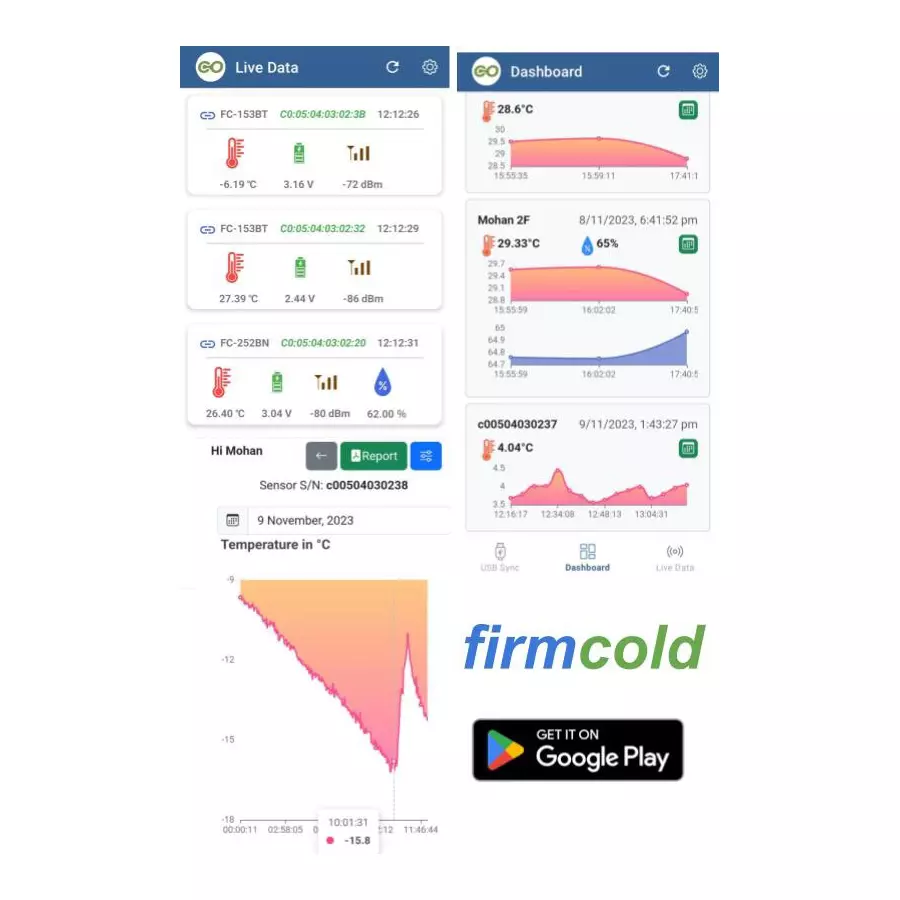
Description
A
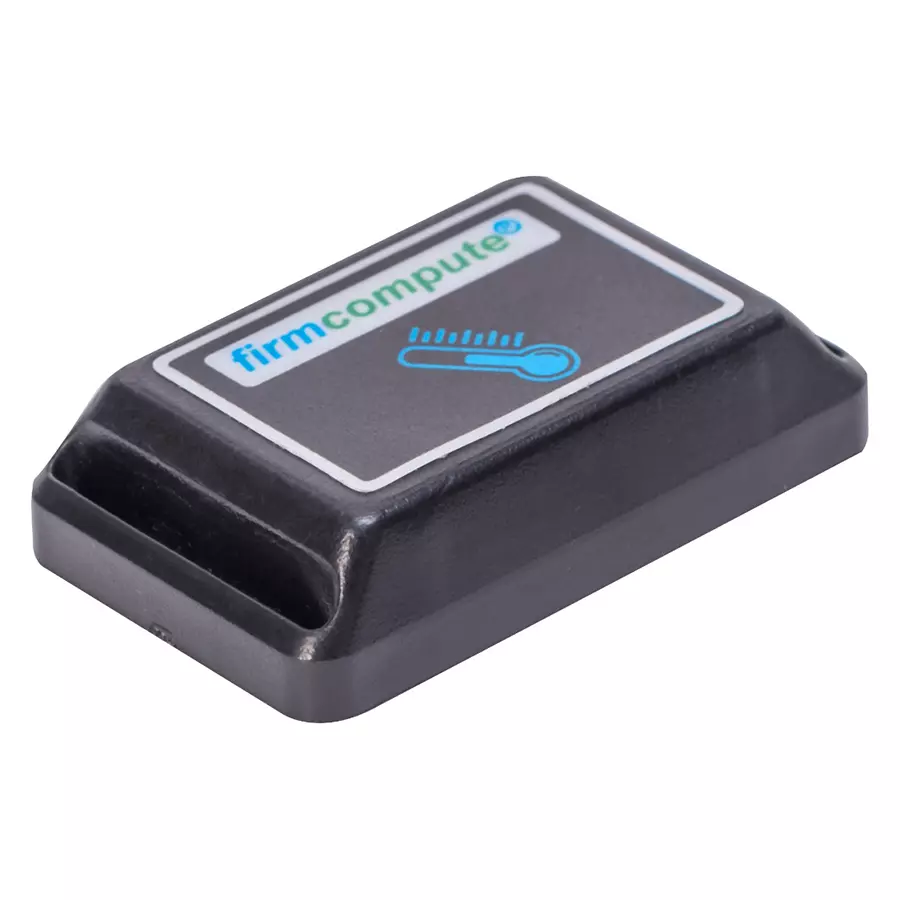
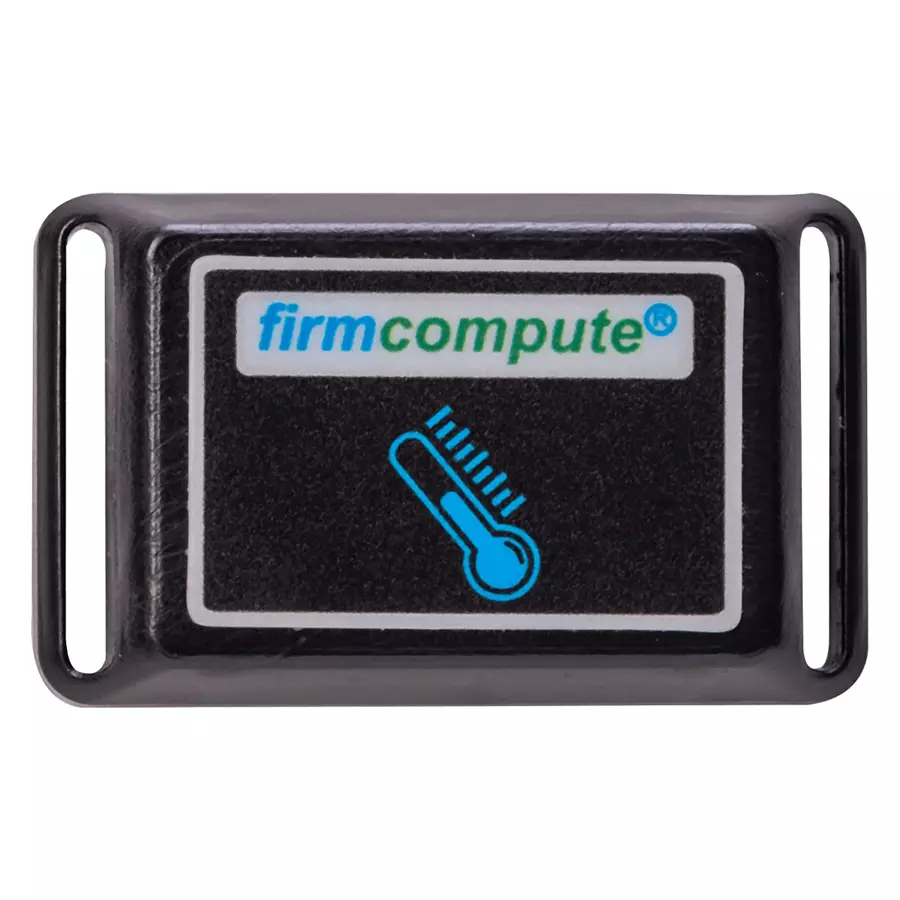
Firmcompute 130 mAh Ultra Small Wireless Temperature Sensor Transmitter, FC-153
BT is a device used to measure temperature and convert the measured temperature
into an electrical signal that can be transmitted to a monitoring or control
system. These transmitters are commonly used in industrial processes, HVAC
systems, laboratory equipment, and other applications where accurate
temperature monitoring and control are essential. Here are the key features and
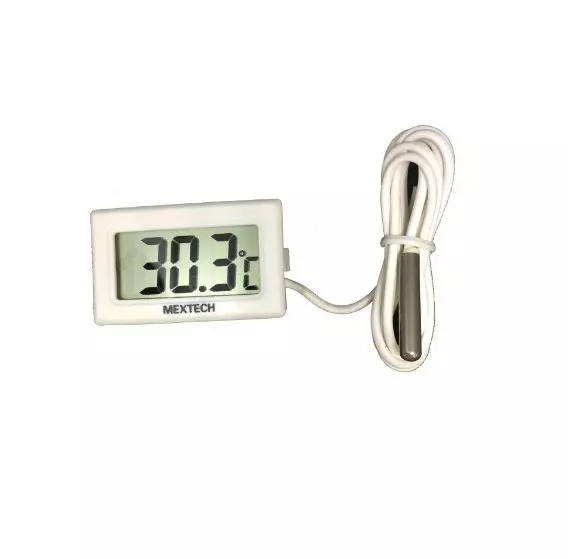
components of a typical temperature transmitter: Temperature Sensor: The
temperature transmitter is equipped with a temperature sensor that detects
changes in temperature and converts them into electrical signals. Common types
of temperature sensors used in temperature transmitters include thermocouples,
resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermistors. Signal Conditioning
Circuitry: The electrical signal generated by the temperature sensor is often
weak and may need to be amplified or conditioned before transmission. Signal
conditioning circuitry within the temperature transmitter processes the raw
sensor signal to ensure accuracy, stability, and compatibility with the
receiving equipment. Output Signal: The output signal of the temperature
transmitter is typically a standardized analog or digital signal that can be
easily interpreted by the receiving equipment.
Common
output signals include 4-20 mA (milliampere) analog signals, 0-10 V (volt)
analog signals, or digital signals such as Modbus, HART, or Foundation
Fieldbus. Housing: Temperature transmitters are housed in protective enclosures
or casings that shield the internal components from environmental factors such
as moisture, dust, and vibration. The housing may be made of materials such as
stainless steel, aluminum, or plastic, depending on the application
requirements. Mounting Options: Temperature transmitters may have various
mounting options to accommodate different installation requirements. They can
be mounted on DIN rails, directly onto equipment or machinery, or integrated
into control panels or cabinets. Calibration: Temperature transmitters are
typically factory-calibrated to ensure accurate temperature measurement.
Some
models may also offer user-adjustable calibration settings to fine-tune the
measurement accuracy as needed. Communication Protocols: Advanced temperature
transmitters may support communication protocols that allow them to interface
with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS),
supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, or other monitoring
and control devices. Temperature transmitters play a crucial role in industrial
automation and process control, providing accurate and reliable temperature
measurement data for monitoring, analysis, and control purposes. By
transmitting temperature information in real-time, these transmitters help
optimize process efficiency, ensure product quality, and enhance safety in a
wide range of industrial and commercial applications.